postgrest使用指南
背景
现在在做的一个app项目,中间service是用postgrest提供api服务(具体文档连接),看文档感觉十分强大,应该满足所有业务逻辑,使用一段时间之后,把postgrest基本用法进行了一个总结。因为相关文档十分稀少,希望对未来用到postgrest的能起到一个参考的作用。
环境搭建
brew doctor
brew update
brew install postgresql
brew services start postgresql
brew install postgrest
可选安装,用户数据库转换,可以把mysql数据库转换成postgresql,非常方便
brew install pgloader
安装之后可以用psql命令进行库的操作,不过本人习惯用pgAdmin4这款终端软件进行管理库,当然知名的Navicat也是可以使用的。
数据库创建
可以利用上面提到的两款工具进行建库,如果已有mysql数据库,可以进行转换:
pgloader mysql://root:007a007b@localhost/pdb pgsql:///demodb
配置文件以及启动服务
任意位置新建db.conf文件,内容如下:
db-uri = "postgres://jianlongnie:@localhost:5432/tdb3"
db-schema = "testapp_db, basic_auth,global_info"
db-anon-role = "jianlongnie"
jwt-secret = "MqQx7uwtxH3JjphNvRzgeQMkNjDt5JzfpqWwNHrQ13c="
log_statement = "all"
运行postgrest -h查看具体解释:
Example Config File:
db-uri = "postgres://user:pass@localhost:5432/dbname"
db-schema = "public" # this schema gets added to the search_path of every request
db-anon-role = "postgres"
db-pool = 10
db-pool-timeout = 10
server-host = "!4"
server-port = 3000
## unix socket location
## if specified it takes precedence over server-port
# server-unix-socket = "/tmp/pgrst.sock"
## unix socket file mode
## when none is provided, 660 is applied by default
# server-unix-socket-mode = "660"
## base url for swagger output
# openapi-server-proxy-uri = ""
## choose a secret, JSON Web Key (or set) to enable JWT auth
## (use "@filename" to load from separate file)
# jwt-secret = "secret_with_at_least_32_characters"
# secret-is-base64 = false
# jwt-aud = "your_audience_claim"
## limit rows in response
# max-rows = 1000
## stored proc to exec immediately after auth
# pre-request = "stored_proc_name"
## jspath to the role claim key
# role-claim-key = ".role"
## extra schemas to add to the search_path of every request
# db-extra-search-path = "extensions, util"
## stored proc that overrides the root "/" spec
## it must be inside the db-schema
# root-spec = "stored_proc_name"
## content types to produce raw output
# raw-media-types="image/png, image/jpg"
所有可选配置,以及解释都非常清楚,端口号等基本配置都可以指定,还是非常灵活的。启动服务:
postgrest db.conf
单表操作
GET查询
GET /people HTTP/1.1
服务器地址:端口号加你所要请求的表明即可,上面people即为表名。
Rows条件
| 条件 | 在PostgreSQL对应 | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| eq | = | equals |
| gt | > | greater than |
| gte | >= | greater than or equal |
| lt | < | less than |
| lte | <= | less than or equal |
| neq | <> or != | not equal |
| like | LIKE | LIKE operator (use * in place of %) |
| ilike | ILIKE | ILIKE operator (use * in place of %) |
| in | IN | one of a list of values, e.g. ?a=in.(1,2,3) – also supports commas in quoted strings like ?a=in.("hi,there","yes,you") |
| is | IS | checking for exact equality (null,true,false) |
| fts | @@ | Full-Text Search using to_tsquery |
| plfts | @@ | Full-Text Search using plainto_tsquery |
| phfts | @@ | Full-Text Search using phraseto_tsquery |
| wfts | @@ | Full-Text Search using websearch_to_tsquery |
| cs | @> | contains e.g. ?tags=cs.{example, new} |
| cd | <@ | contained in e.g. ?values=cd.{1,2,3} |
| ov | && | overlap (have points in common), e.g. ?period=ov.[2017-01-01,2017-06-30] – also supports array types, use curly braces instead of square brackets e.g. :code: ?arr=ov.{1,3}sl<<strictly left of, e.g. ?range=sl.(1,10)sr>>strictly right ofnxr&<does not extend to the right of, e.g. ?range=nxr.(1,10)nxl&>does not extend to the left ofadj`- |
| sl | << | strictly left of, e.g. ?range=sl.(1,10) |
| sr | >> | strictly right of |
| nxr | &< | does not extend to the right of, e.g. ?range=nxr.(1,10) |
| nxl | &> | does not extend to the left of |
| adj | -|- | is adjacent to, e.g. ?range=adj.(1,10) |
| not | NOT | negates another operator, see below |
用法:
GET /people?age=gte.18&student=is.true HTTP/1.1
查询年龄大于18并且是学生的。
逻辑或逻辑与
GET /people?and=(grade.gte.90,student.is.true,or(age.gte.14,age.is.null)) HTTP/1.1
如果以上不能满足你的需求你可以通过建视图的方式来查询:
CREATE VIEW fresh_stories AS
SELECT *
FROM stories
WHERE pinned = true
OR published > now() - interval '1 day'
ORDER BY pinned DESC, published DESC;
GET /fresh_stories HTTP/1.1
列查询
GET /people?select=first_name,age HTTP/1.1
[
{"first_name": "John", "age": 30},
{"first_name": "Jane", "age": 20}
]
重命名列
GET /people?select=fullName:full_name,birthDate:birth_date HTTP/1.1
[
{"fullName": "John Doe", "birthDate": "04/25/1988"},
{"fullName": "Jane Doe", "birthDate": "01/12/1998"}
]
类型转换
GET /people?select=full_name,salary::text HTTP/1.1
[
{"full_name": "John Doe", "salary": "90000.00"},
{"full_name": "Jane Doe", "salary": "120000.00"}
]
分页
GET /people?limit=15&offset=30 HTTP/1.1
header里面添加Prefer: count=exact可返回数据总条数:
HEAD /bigtable HTTP/1.1
Range-Unit: items
Range: 0-24
Prefer: count=exact
HTTP/1.1 206 Partial Content
Range-Unit: items
Content-Range: 0-24/3573458
返回格式
GET /people HTTP/1.1
Accept: application/json
可选格式
*/*
text/csv
application/json
application/openapi+json
application/octet-stream
嵌套查询(最多支持两个表连动)
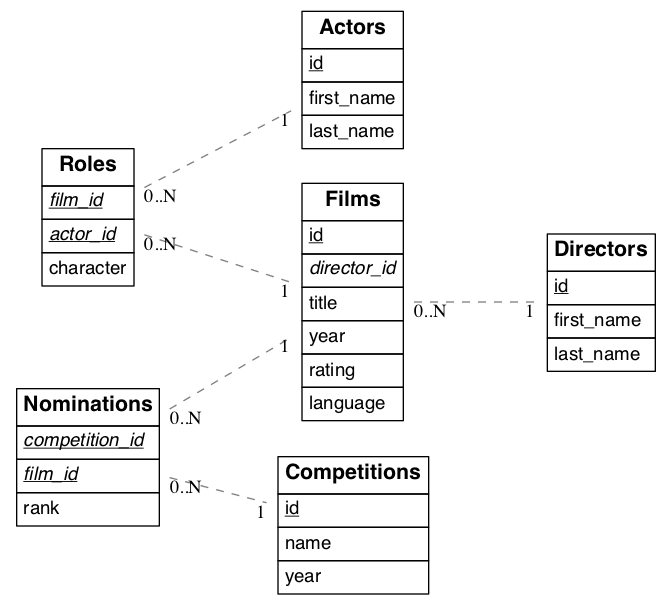
films和directors有一个一对一的外键关联,其查询就非常简单:
GET /films?select=title,directors(id,last_name) HTTP/1.1
结果
[
{ "title": "Workers Leaving The Lumière Factory In Lyon",
"directors": {
"id": 2,
"last_name": "Lumière"
}
}
]
多关联外键的查询

图中表有两个外键关联,这时候查询的时候需要制定外键的名字,不然postgrest不知道通过那个外键进行查询,图中外键如下:
ALTER TABLE orders
ADD CONSTRAINT billing_address foreign key (billing_address_id) references addresses(id),
ADD CONSTRAINT shipping_address foreign key (shipping_address_id) references addresses(id);
-- Or if the constraints names were already generated by PostgreSQL we can rename them
-- ALTER TABLE orders
-- RENAME CONSTRAINT orders_billing_address_id_fkey TO billing_address,
-- RENAME CONSTRAINT orders_shipping_address_id_fkey TO shipping_address;
其查询变为:
GET /orders?select=name,billing_address:billing_address_id(name) HTTP/1.1
[
{
"name": "Personal Water Filter",
"billing_address": {
"name": "32 Glenlake Dr.Dearborn, MI 48124"
}
}
]
嵌套查询
看上面的图,actors和films是通过roles进行关联的,可以通过以下方式查询:
GET /actors?select=films(title,year) HTTP/1.1
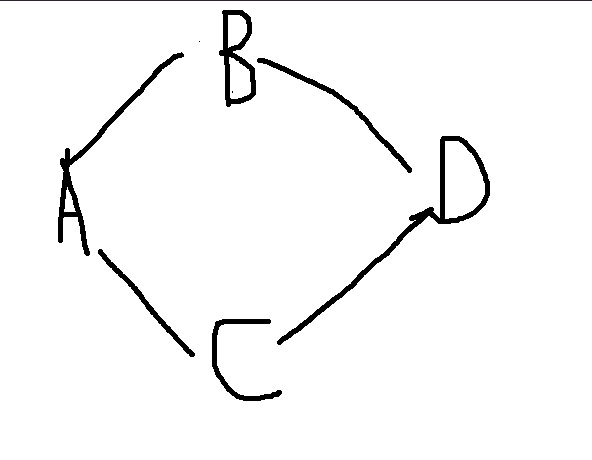
如果有a、b、c、d四张表,他们关系如上图:
目前是这样的一个引用状态,这样a想取d里面的数据的时候,postgrest就不知道通过b还是c来取d,所以就会不成功。那该怎么解决呢?

切断b或者c其中一个和d之间的联系即可。
嵌套多表查询
还是上图中关系,a、b、c、d四张表,要取和a相关连的d以及c的数据:
/A表?select=*,D表(*),C表!A表C表外键名称(*)
如果还有e表、f表,也可以继续查询:
/A表?select=*,D表(*),C表!A表C表外键名称(*),E表!A表E表外键名称(*)
所以说功能还是十分强大的。
数据插入
插入一条数据用post请求,
POST /table_name HTTP/1.1
{ "col1": "value1", "col2": "value2" }
这样请求结果,成功的时候body不会返回任何结果,若要body返回插入item结果,需要在header里面添加Prefer: return=representation
数据更新
更新某一列用patch
PATCH /people?age=lt.13 HTTP/1.1
{ "category": "child" }
若要body返回插入item结果,需要在header里面添加Prefer: return=representation
数据删除
若要返回删除item信息,需要在header里面添加Prefer: return=representation
DELETE /user?id=eq.1 HTTP/1.1
Prefer: return=representation
{"id": 1, "email": "johndoe@email.com"}
切换schema
由于业务场景需要,程序还可能要动态访问多个schema,
配置文件
配置文件中需要列出多有可访问的schema:
db-uri = "postgres://jianlongnie:@localhost:5432/tdb3"
db-schema = "testapp_db, basic_auth,global_info"
db-anon-role = "jianlongnie"
jwt-secret = "MqQx7uwtxH3JjphNvRzgeQMkNjDt5JzfpqWwNHrQ13c="
log_statement = "all"
上面就是支出可以访问testapp_db, basic_auth,global_info三个schema,这只是第一步,若要实现动态需要在header里面指定schema:
GET /items HTTP/1.1
Accept-Profile: basic_auth
get请求的时候添加Accept-Profile加schema,其他请求添加Content-Profile加schema。
POST /items HTTP/1.1
Content-Profile: tenant2
{...}
自定义api
如果以上功能都不能满足你的需求,postgrest还有绝招:自定义存储过程。
create or replace function 过程名(参数名 参数类型,…..) returns 返回值类型 as
$body$
//声明变量
Declare
变量名变量类型;
如:
flag Boolean;
变量赋值方式(变量名类型 :=值;)
如:
str text :=值; / str text; str :=值;
Begin
函数体;
return 变量名; //存储过程中的返回语句
End;
$body$
Language plpgsql;
声明格式如上:
create or replace function testapp_db.f_get_categoty_detail(in sign varchar)
returns setof testapp_db.result_t
as
$$
begin
return query select s.*, amb.*, ls.*
from testapp_db.app_subjects as s left join
testapp_db.subject_snapshot as ss on s.subject_sign = ss.subject_sign
left join testapp_db.app_labels as ls on s.subject_label_sign = ls.label_sign
left join testapp_db.app_material_bank as amb on amb.material_sign = ss.material_sign
where s.subject_sign = sign;
end;
$$
language plpgsql
以上就是创建了一个testapp_db下面的名字叫f_get_category的函数,其返回类型可以是各种postgresql 基础类型,以及表类型等,但是需要注意的是你的select返回值一定要和返回类型对应起来,如果你的返回类型比较特殊,比如多表查询之后返回的类型,这个时候返回的类型就需要你创建一个新类型来接受返回的数据,比如上面例子,我们要返回三个表的column,那我们就要新建类型:
create type testapp_db.result_type as (
subject_id bigint,
subject_sign varchar(100) ,
subject_name text ,
subject_intro text,
bundle_price varchar(20),
is_only_test bool,
is_only_cert bool,
is_content bool,
subject_label_sign varchar(100),
is_to_c bool,
top_block_order int4,
middle_block_order int4,
bottom_block_order int4,
sdelete_flag boolean,
create_time timestamp ,
update_time timestamp ,
material_id bigint,
material_url varchar(1024) ,
material_sign varchar(100) ,
title text ,
sub_title text ,
summary text ,
test_question_amount int4,
m_delete_flag bool,
lcreate_time timestamp,
ulpdate_time timestamp,
label_id bigint,
label_sign character varying(100) ,
label_fullname text,
superlabel_sign character varying(100),
label_order integer,
delete_flag boolean,
hhcreate_time timestamp ,
hhupdate_time timestamp
);
最简单的方式就是把所有表字段放到一块,简单粗暴!存储过程中字符串操作方式也非常灵活
o_area := replace(o_area,in_id,'') || '~' || replace(v_rec_record.label_sign,in_id,'');
拼接符号||,字符串方法replace、split等都可以使用,非常强大!
DROP FUNCTION testapp_db.f_get_categoty_detail(character varying);
要删除一个存储过程可以用上面的语句,测试存储过程用下面这条语句:
select testapp_db.f_get_categoty_detail('product');
总结
以上应该除了用户鉴权的介绍之外,增删改查都基本可以满足业务需要,由于用户鉴权即jwt还是比较麻烦的,打算单独拿出一遍文章来进行介绍,
create type testapp_db.content_children as (
label_id bigint,
label_sign character varying(100),
label_fullname text,
superlabel_sign character varying(100),
label_order integer,
delete_flag boolean,
create_time timestamp,
update_time timestamp,
material_id bigint,
material_url character varying(1024),
material_sign character varying(100),
title text,
sub_title text,
summary text,
test_question_amount integer,
mdelete_flag boolean,
mcreate_time timestamp,
mupdate_time timestamp
);
user=> (distinct [1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5])
(1 2 3 4 5)
(:material_url (js->clj row :keywordize-keys true))